The meaning of broadband satellites
Internet connection brings many benefits, improving the quality of life for people. When using the Internet at home, it is almost certain that users are using a form of broadband. Broadband can be defined according to different standards and speeds, but broadband must be at least sufficient to allow the transmission of an HD standard video, play online games and allow sending and receiving large amounts of data.
There is the fact that nearly two-thirds of the world does not have internet access. This is due mainly broadband internet provided by terrestrial network that will be unable or very difficult deployed in areas such as islands, desert terrain... This is a reason for technology companies to work non-stop to find solutions to provide internet for two-thirds of the world without internet. The solution is given as "internet from the sky" through means such as balloons, unmanned crafts or satellites. The companies will have the opportunity to provide their products and services to new large markets.
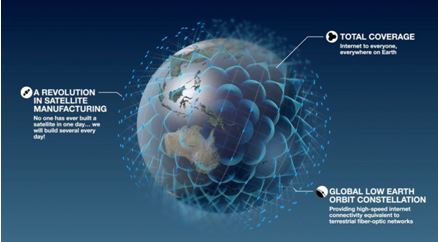
With the strong development of technology, great aspirations and ambitions, a new era for broadband Internet satellite service is likely to open, with the flagship of SpaceX. If SpaceX's test model succeeds, in the near future tens of thousands of satellites will be launched into orbit. Broadband Internet service is provided everywhere, every corner of urban and rural areas, islands, hills, deep-lying, remote, desert areas with very cheap cost. It is an opportunity but also a challenge that upsets the "telecommunications world" order.
SpaceX 's satellite consellation project
2015, Elon Musk began deployment system testing "Broadband Global", and in September 2017 it had filed registration satellite network broadband called Starlink with the agency's telecommunications USA (FCC), with the goal of building a low-cost broadband satellite network capable of providing global internet access.
With Starlink, SpaceX plans to launch "cluster" of satellites in low earth orbit LEO, providing high-speed Internet to every "nook and cranny" of the planet. The project is expected to cost about US $ 10 billion, fully operating the system by 2024. At first, SpaceX will have launched 4.425 satellites to achieve the desired coverage.
On February 22, 2018, SpaceX successfully launched the first two Starlink test satellites (Tintin A and Tintin B). The satellites was designed primarily test and evaluation system whether feasible Starlink or not.
 In March 2018, the FCC approved the official request for a broadband service project, spaceX was provided with services in the United States. In the first phase only about 800 satellites are expected to be launched.
In March 2018, the FCC approved the official request for a broadband service project, spaceX was provided with services in the United States. In the first phase only about 800 satellites are expected to be launched.
There is information about SpaceX deploying 03 packages for consumers to choose, including: StandardX, PremiumX and ProfessionalX, with "super cheap" monthly subscription prices of 9.99 USD, 19.99 USD and 29.99 USD.
With StandardX, users are provided with a capacity of 1000 GB /month at a rate of 10,000 Mbps to access, including text messaging with short global content + voice. An additional $10/month will receive PremiumX package with a capacity of 2000 GB/month and speeds of 20.000 Mbps, allowing unlimited texting globally. More advanced, ProfessionalX does not limit capacity with super fast access speeds of 1,000,000 Mbps. Although there has not been an official announcement about the price of the package from SpaceX, this has also raised concernsfor global geostationary satellite service providers and mobile operators.
Some other projects
Project of Facebook satellite concellation
Facebook is developing a satellite called "Athena" to provide Internet service for underdeveloped areas. Athens is expected to be launched early next year test. If the test is successful, Facebook will launch a satellite network such as Starlink model.
Prior to this project, Facebook had to abandon the project to provide broadband Internet with unmanned aircraft (internet drone Aquila aircraft) after 04 years of testing not being as successful as expected.
Project of OneWeb satellite concellation
OneWeb has joint venture with Airbus to build a satellite beam system of 900 satellites.
SpaceX and OneWeb are direct competitors. OneWeb and SpaceX have the same goals, but their organizations don't match. SpaceX integrates itself, building rockets, satellites and ground stations, while OneWeb has project implementation partners such as Qualcomm who designs and supplies communication chips, Airbus manufactures satellites.
OneWeb has a symbiotic relationship with Softbank, their biggest investor. SoftBank's Vision Fund has invested $1 billion into OneWeb.

OneWeb expects price per satellite less than 1 million USD and can be produced every day three satellites. The first satellites have a capacity of 595 Mbps, then will increase to over 1 Gbps.
2017 OneWeb had registration filing with the FCC launched 720 satellites orbit with the height of 1,200 km and 1,280 satellite at an altitude of 8,500 km.
OneWeb plans to launch its first 10 satellites in March 2018, which is expected to begin service in Alaska state in 2019 and will cover all Alaska by the end of 2020. By 2025 they are expected. There will has 1 billion subscribers, global coverage by 2027. However, the plan to launch satellites was delayed until the end of 2018, early 2019.
Project of O3B satellite concellation
Satellite company SES leading O3B now owns the tumor. On June 8, 2018, the FCC has allowed SES to provide services with the addition of 26 medium-range MEO satellites that increase the total number of MEO satellites to 42 satellites (16 active satellites) that can be provided global service. Four new satellites will be launched next year, orbit 8000Km.
Project of Telesat satellite concellation
Telesat is licensed by the United States to release 117 LEO satellites, which will launch ½ of these satellites in the first six years and all satellites in 09 years.
However, the company plans to launch more with 512 LEO satellites to provide services and has signed a satellite production contract with Airbus Defense and Space and axar Technologies / Thales Alenia Space in the Ka band.
Conclude
Currently only about 1,459 satellites are active in orbit around the earth, along with 2600 is no longer active. However, the number of satellites is expected to be greatly enlarged. Total expected satellite consellations for the global Internet project around the next few years: 18,470 satellites, operating in the C, Ku, Ka and V bands (Ka here indicates band 26- 40GHz). There are 18 companies/corporations developing this model, including big names such as:
- SpaceX: expects to launch 12,000 satellites.
- Airbus and OneWeb: expected to launch 900 satellites.
- Boeing: expects to launch 2956 V-band satellites, 60 Ka band satellites.
- Samsung: expected to release 4600 satellites.
- Telesat (Canada): expects to launch 120 satellites by 2021, launching its first satellite test in 1/2018, towards global service delivery.
- Leosat: expects to launch 78-108 LEO satellites Ka expected to launch 2019.
- O3b: expected to release 24 MEO satellites.
- Visat: expected to release 24 MEO satellites.
This shows that there is a strong race between large technology corporations in "covering" sky-filled satellites to provide broadband Internet services to every corner of the world. The truly flat world with billions of people on this green planet will not be far away
MSc. Nguyen Huy Cuong
References:
1] SpaceX's Prototype Internet Satellites Are Up and Running, Mike Wall, Space.com Senior Writer
[2] New satellite constellations will soon fill the sky by Staff Writers for Launch space Bethesda MD (SPX) Jul 17, 2018
[3] SpaceX to in-house mass production of Starlink internet satellite hardware, By Eric Ralph, June 4, 2018
[4] 4 billion people still don’t have internet access. Here’s how to connect them, Emma Luxton, Formative Content